Direct Internet Access (DIAS)
What is it?
- Offers a wire-line solution for high-speed symmetrical Internet aaccess on the existing telephone lines.
- Provides an " Always On" Internet Access that is permanently available at the customer's premises.
- Combines voice and Internet data packets on a single twisted-pair wire at the subscriber's premises
Schematic diagram of a DIAS system:
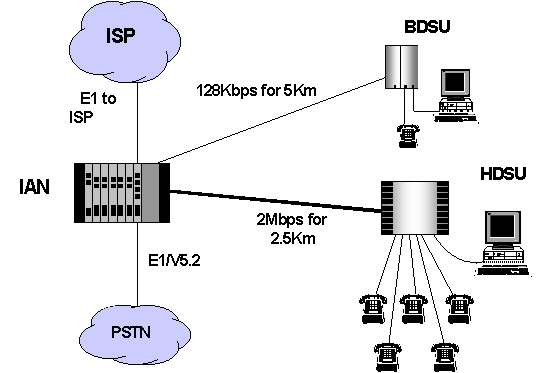
What does it have?
- Basic Digital Subscriber Unit BDSU) - At customer's premises
- Internet Access Node (IAN ) - at the BSNL Exchange.
Functions of IAN
- Separates Voice and Data traffic from a number of subscribers (60 in each IAN)
- Routes independently to the PSTN (over V 5.2) and Internet respectively (E1 data ports or Ethernet ports) using E1 links.
- Acts as an access unit of the Exchange and provides all the features and services of the Exchange to the Subscriber.
- Provides 64 Kbps / 128 Kbps connectivity to the Internet via one E1 link (maximum concentration of 8 : 1).
What does the IAN do
- Separates the Voice traffic and the Internet traffic
- The voice traffic from each BDSU/ HDSU is circuit switched on demand to one of the 64kbps slots on E1 lines connected to an Exchange
- The protocol used between the IAN and the switch is the standard V5.2. optionally the IAN can have a SMUX unit, which would connect the DIAS subscriber to the exchange on 2-W interface
Thus, the IAN acts as an ACCESS UNIT of the exchange and provides the services of the Exchange to the subscriber.
The Internet traffic from each BDSU/HDSU is concentrated at the IAN (IAN essentially acts as a Remote Access Server - RAS, at this point) and passed on to the ISP on a 10 Mbps Ethernet or an E1 leased line. Up to two such E1 ports are provided on the IAN for connection to the ISP.
Integrated Access Node (IAN) at the Exchange
- Separates voice and data traffic from a number of subscribers
- Routes them independently to the PSTN and the Internet respectively.
- Connected to the PSTN via an E1 voice ports to the Internet either through E1 data ports or through an Ethernet port.
- Protocol used between the IAN and the switch is the ITU standard V5.2
- Voice traffic from each BDSU is circuit switched on demand to one of the 64kbps slots on E1 lines connected to an Exchange essentially acts as a Remote Access Server – RAS, at this point) line. Up to two such E1 ports are provided on the IAN for connection to the ISP
- Internet traffic from each BDSU/HDSU is concentrated at the IAN.
- Multiple IANs could also be cascaded at the Exchange premises.
Basic Digital Subscriber Unit
- Designed for the SOHO (Small Office Home Office) and the residential Internet user.
- Provides a permanent Internet connection at a maximum data rate of 128 kbps, which drops to 64 kbps when the telephone is in use and transprently goes back to 128 kbps when the telephone goes on-hook.
- Located at the subscriber's premises has a telephone interface (RJ11) and an Ethernet port (RJ45) to provide Internet Access.
- Has local powering off the AC Mains (110V/230V) and a backup battery to support the telephone on power failure.
- Ethernet port providing Internet access is off during power failure.
Typically, the battery back up gives 8 hrs of standby time and 4 hrs of talk time.
Basic Digital Subscriber Unit ( BDSU)
- Combines voice and Internet data packets on a single twisted-pair wire at the subscriber’s premises.
- Provides a permanent Internet connection at a maximum data rate of 128 kbps, which drops to 64
kbps when
the telephone is in use and transparently, goes back to 128 kbps when the telephone goes on- hook. - Located at the subscriber's premises has a telephone interface (RJ11) and an Ethernet port (RJ45) to provide Internet Access. has local powering off the AC Mains (110V/230V) and a backup
- battery to support the telephone on power failure. The Ethernet port providing Internet access is off during power failure. Typically, the attery back up gives 8 hrs of standby time and 4 hrs of talk time.
- connected to the Integrated Access Node, located either at a street corner (curb) or at the Exchange, using a twisted pair copper wire.
- the maximum length of the copper can be 5 km when 0.5-mm twisted pair copper is used.
- has a minimum routing function built-in and routes the packets on the Ethernet meant for ISP on to the IAN.
What is a HDSU ?
High bit rate Digital Subscriber Unit
- Designed for Corporate subscribers .
- Can provide voice connectivity for up to 8 telephones and - permanent data connectivity of up to 2 Mbps, which drops to 512Kbps when all the 8 telephones are in use.
- Has an Ethernet port and 4/8 Telephone Interfaces (RJ11) thus having the ability to connect to 4 or 8 independent telephones at a Corporate office.
Connection of BDSU and HDSU
BDSU and the HDSU - connected to the Integrated Access Node (IAN) located either at a street corner (curb) or at the Exchange, using a twisted pair copper wire.BDSU - Max. length of the copper can be 5 km when 0.5- mm twisted pair copper is used.
HDSU
- Connected using copper to the IAN.
- Maximum rate at which Internet Access is provided to the
- HDSU Ethernet port is 2 Mbps
- Length of the copper < 2.5 Km (0.5mm twisted pair copper)
- the bit-rate on the HDSU-IAN link drops for higher lengths of copper, thus reducing Internet access rate on the HDSU Ethernet port.
Both the HDSU and the BDSU have a minimum routing function built-in and routes the packets on the Ethernet meant for ISP on to the IAN.




